The connections in steel structures are extremely important in the construction process. Therefore, choosing the appropriate method for steel connection will help ensure the safety of the project as well as optimize costs and raw materials. Let’s explore some types of connections in steel structures and their advantages and disadvantages with Pebsteel.
1. What are the connections in steel structures?
Connections in steel structures are crucial elements in the structural steel building. Steel connections include parts such as nails, bolts, and welding, which serve to connect two or more steel components. They can also be used to join steel buildings to other types of construction, such as brick or concrete blocks. The load-bearing capacity and strength of steel connections depend on the installation method. Proper installation is a crucial factor in ensuring that the connection functions effectively.
2. Classifications of connections in steel structures
There are three most common types of connections in steel structures: welded connections, bolted connections, and riveted connections. Among them, riveted connections are used less frequently due to difficulties in disassembly.
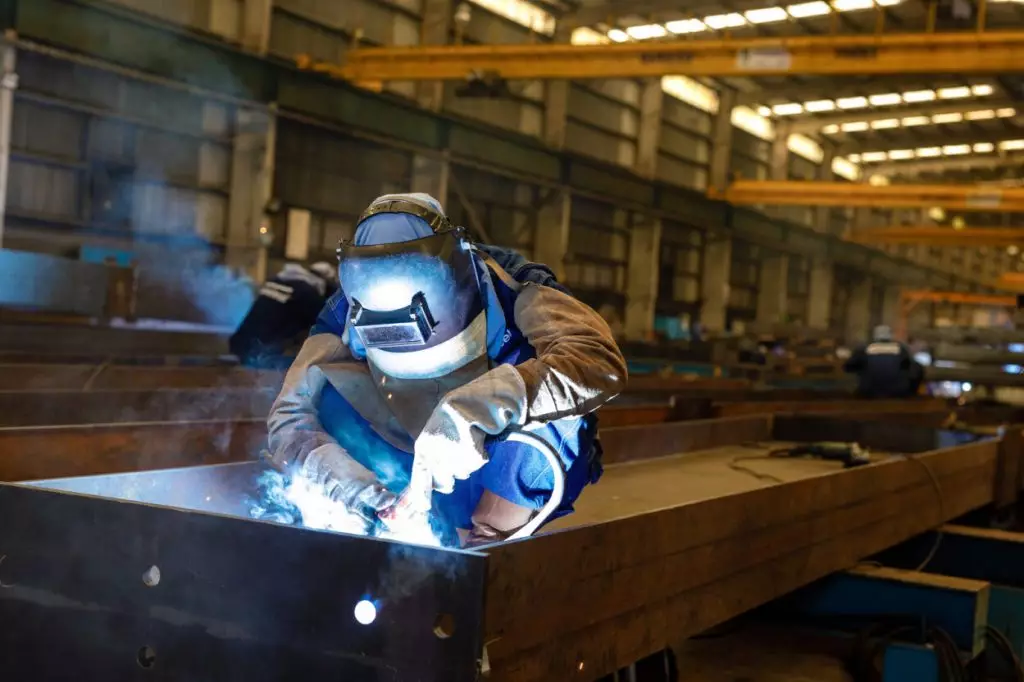
2.1. Welded connections
Welding is a commonly used method in the production of steel structures. This method utilizes heat (through flames or electric arcs) to locally heat the metal at the contact point until it melts and gradually blends. After cooling, this metal part will slowly solidify, forming the weld.
The classifications of welded connections:
- Manual Electric Arc Welding
- Automatic Electric Arc Welding
- Semi-Automatic Welding
- Gas Welding
Welded connections have the following advantages:
- Joining efficiency of up to 100%.
- Applicable to complex steel structures.
- Low noise generation.
- Time-saving and cost-effective.
- Lightweight, causing minimal stress on the steel structure.
Some disadvantages of welded connections:
- There is a risk of deformation to the steel structure due to the heating process.
- Welds are prone to cracking and breaking.
- Welded connections require skilled labor.
- Quality inspection of welds can be relatively challenging.
- Base metal may experience metal fatigue below the welding point.

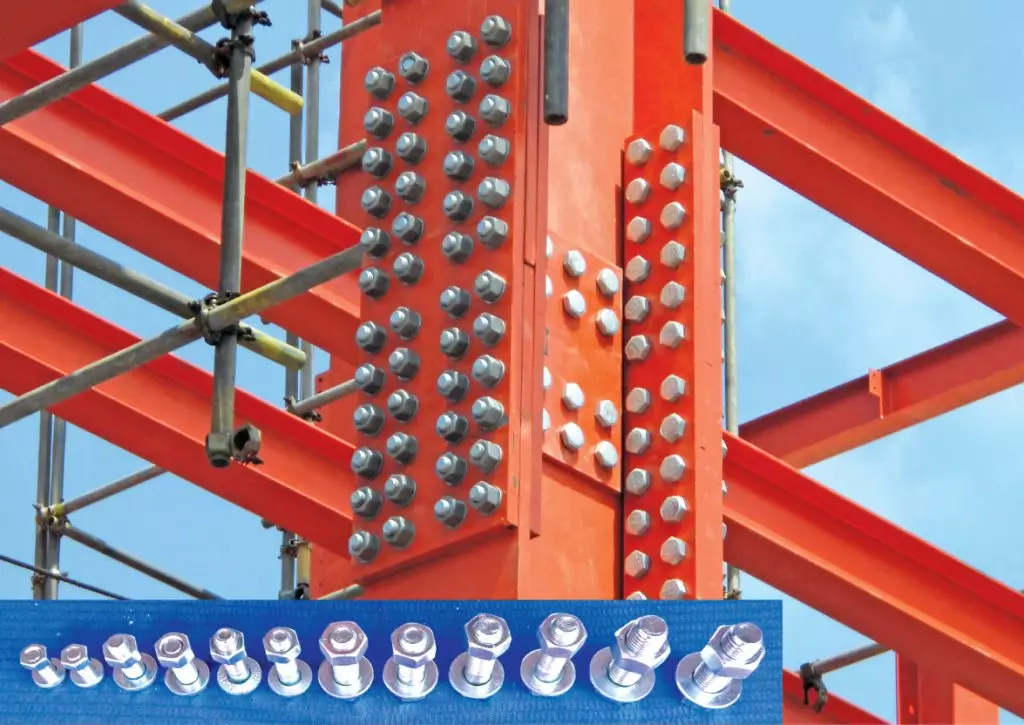
2.2. Bolt connections
Bolt connections in steel structures have been popular for a long time. This type of connection is established by fastening two components together using bolts and heavy-duty nuts. Bolted connections can be easily assembled or disassembled, which greatly facilitates regular inspection and maintenance. They can be applied to components subjected to tension, shear, or even both.
Based on the synthesis of transfer forces, bolted connections are divided into three types:
- Concentric connections
- Eccentric connections
- Moment resisting connections
Based on the type of force, bolted connections are divided into three types:
- Shear connections
- Tension connections
- Combined tension shear connections
Based on the force mechanism, bolted connections are divided into two types:
- Bearing-type connections
- Friction-type connections
Some advantages of bolted connections:
- The structure assembly process is quick.
- It does not require highly skilled labor.
- It does not generate much noise during implementation.
- The structure can be used immediately after the bolted connection is made.
- It allows for the arrangement and replacement of structural components if necessary.
Some disadvantages of bolted connections:
- The cost of materials is relatively high.
- Bolted connections are less durable due to their reduced threaded area and susceptibility to stress concentration.
- Bolts can become loose when subjected to external impacts.
2.3. Riveted connections
Riveted connections are similar to bolted connections in that both use a type of component to join various elements together. This technique involves placing rivets into the openings of the components that need to be connected and fastening the end of the rivet to ensure the components remain intact. However, riveted connections are a rather old method and are less commonly used in practical applications these days.
Rivets are divided into four types:
- Hot-driven rivets
- Shop rivets
- Field rivets
- Cold-driven rivets
The advantages of rivet connections:
- Rivet connections are extremely sturdy.
- The durability of rivet connections is very high, making them suitable for large-scale projects.
The disadvantages of rivet connections:
- They generate a lot of noise during installation.
- Inspecting the quality of the connection requires highly skilled labor.
- Both the installation and disassembly processes consume a significant amount of time and cost.
3. Conclusion
Above is information about various types of connections in steel structures, as well as their advantages and disadvantages. If customers need comprehensive solutions for Pre-engineered Steel Buildings and Steel Structures, please get in touch with Pebsteel via email at pebsteel.indonesia@pebsteel.com for immediate consultation.
*** This article is intended to provide general information about the pre-engineered steel building and steel structure industry only. For further details or clarification based on your needs, please contact Pebsteel directly.







